Countdown to Catastrophe: What Nobody Is Telling You About the Imminent Eruption of the Major US Volcano
So, here’s a curveball for your usual weather chatter: lurking nearly 300 miles off the Oregon coast is the Axial Seamount—an underwater volcano that’s been playing peekaboo with the Pacific Ocean since at least the late ’90s. Scientists have raised their eyebrows recently, warning that this giant, which has erupted before in ’98, 2011, and 2015, might be ready to stir up some action again—maybe sooner than you’d think. Now, before you start picturing a scene straight out of a disaster movie with lava fountains threatening the mainland, hold onto that popcorn. This volcano’s a deep-sea character, tucked away 4,900 feet below the surface, which means its drama is likely to stay under wraps—literally—and probably won’t send shockwaves to your living room. But here’s the kicker: How does a volcano that’s been quietly bubbling under the ocean floor impact the environment and marine life above? And could its next move turn out to be something none of us imagined? Let’s dive into what we know—and what remains delightfully uncertain. LEARN MORE
Scientists in the US have recently warned that a major volcano is close to erupting and could do so imminently.
This isn’t the first time that the Axial Seamount volcano has erupted, with previous eruptions happening in 1998, 2011, and 2015.
But, of course, the recent warning has left many wondering when the volcano will erupt, whether the effects will be felt on the US mainland, and what impact it will have on the local environment.
Where is the volcano?
The Axial Seamount is a submerged volcano which is located in the Pacific Ocean, around 480km (298 miles) west of Cannon Beach, Oregon.
The volcano stands at an impressive 1,100 metres above the seafloor and is the youngest active volcano on the Juan de Fuca Ridge.

The Axial Seamount is located more than 4,900 feet below the surface of the Pacific Ocean (Smithsonian Institute)
According to National Geographic, the Juan de Fuca Ridge is ‘where two tectonic plates go their separate ways and fresh magma can bubble up from inside the planet’.
When do scientists predict it will erupt?
A recent increase in seismic activity across the US’ West Coast has prompted scientists to believe that the volcano will erupt by the end of 2025.
As per the New York Post, Oregon volcanologist Bill Chadwick, who has studied the seismic activity in the area, recently stated: “What’s leading us to talk about an eruption in the next year and by the end of 2025 is we’re almost fully reinflated to the level it was before the 2015 eruption.”
The increase in earthquakes within the area, alongside recently identified pools of magma beneath the volcano, indicates that it could be ready to blow its load at any given moment.
However, Chadwick added that there’s ‘no certainty’ to Axial Seamount’s next move and there’s the possibility that it does ‘something different that we haven’t seen before’.
Will it be felt on US mainland?
As the Axial Seamount is located nearly 300 miles from the nearest coast, scientists believe that it’s extremely unlikely that any eruption would be felt on the US mainland.
On top of its remote location, the submerged volcano is located deep below the ocean, where any eruptions usually involve the effusion of lava.
So if you were hoping to see epic spewing lava like the end of Star Wars: Episode III – Revenge of the Sith, it’s bad news, I’m afraid – seamounts are much less spectacular for those of us on dry land.
In fact, it’s likely that the volcano will erupt without anyone in the US actually noticing it (unless, of course, they’re a scientist or someone studying it).
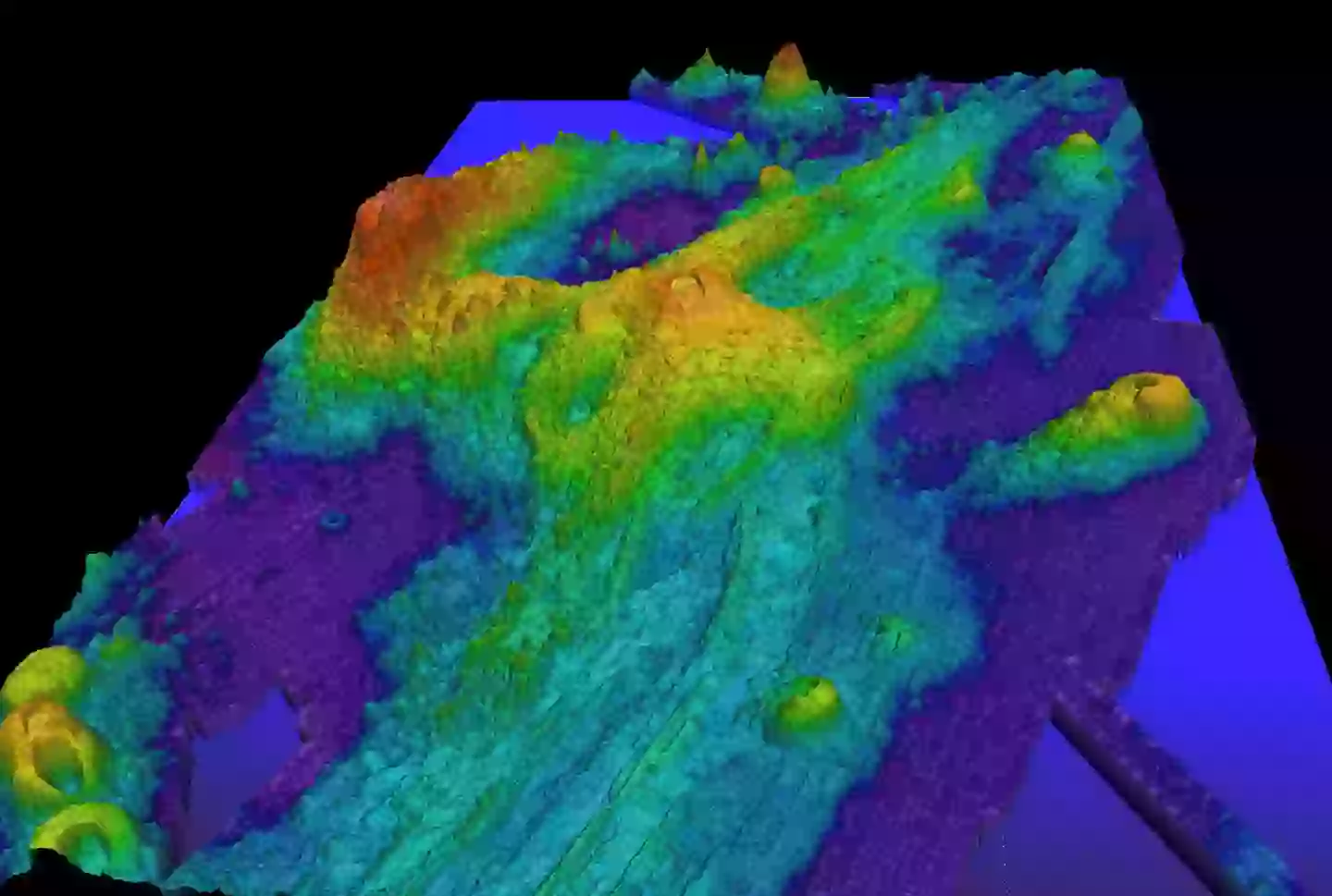
The eruption is expected to impact the topography of the surrounding area (NOAA)
What damage will it cause to the surrounding area?
If you’re worried about what impact the eruption will have on its vicinity, fear not, this too is a little less epic than you might think.
The eruption is predicted to cause minimal damage to the surrounding area and isn’t expected to cause any major threats, such as tsunamis.
Deep-sea volcanoes usually result in new lava flows on the seafloor, which often alter the seafloor’s topography, without causing any serious damage.
What impact will it have on marine life?
Scientists suspect that the eruption is likely to cause temporary disruption to marine ecosystems, however, they also expect that marine life in the area will make a quick recovery.
Studies from previous eruptions have shown the main impact is on hydrothermal vent communities, but these have rebounded over time, giving us no cause for concern over marine life when it comes to the expected eruption.
In contrast to what you might expect, deep-sea eruptions can actually foster the growth of new biological communities that thrive in extreme conditions, bringing life from the chaos and destruction of the volcano.

















