Secret Simulation Reveals Chilling Reality of Nuclear Bombs Amid Escalating Global Crisis
Ever wonder what makes an atomic bomb tick? No, it’s not something you can just unpack and throw into a backyard barbecue, though given the current global tensions, that might feel about as reassuring. Just last night, amid the riotous back-and-forth between Iran and Israel—where ceasefires flicker out faster than you can say “not again”—a viral simulation showed us right down to the atom, literally, how these warheads unleash chaos. President Trump himself was so baffled by the ceasefire shenanigans that he let loose a heartfelt F-bomb on live TV. And honestly, can you blame him? With the U.S. dropping warheads on Iranian air bases and rage bouncing back to American bases in Qatar and Iraq, the stakes are comically apocalyptic. While folks might have watched Oppenheimer and nodded along, who really wants a three-hour dive into neutrons and isotopes? This simulation cuts through the jargon, showing the raw, terrifying mechanics behind nuclear fission—the stuff that makes atomic bombs both fascinating and utterly chilling. Ready to see how the fallout really unfolds? LEARN MORE
A harrowing simulation that shows how an atomic bomb actually works has gone viral amidst growing tensions around the world.
Last night, President Donald Trump announced that a ceasefire had been agreed between Iran and Israel, however, it was seemingly short lived as Israel soon claimed that Iran violated the ceasefire with an attack of their own, though Trump said to media that he was ‘not happy’ with Israel either as it was reported that they too fired at Iran.
The US President was so perplexed by the nations in fact, that the 79-year-old dropped an F-bomb on live TV when speaking about the supposed ceasefire.
The decision came following events at the weekend, which saw the US drop warheads on Iranian air bases, before they retaliated and hit US bases in Qatar and Iraq.
Why are people concerned about nuclear warfare?
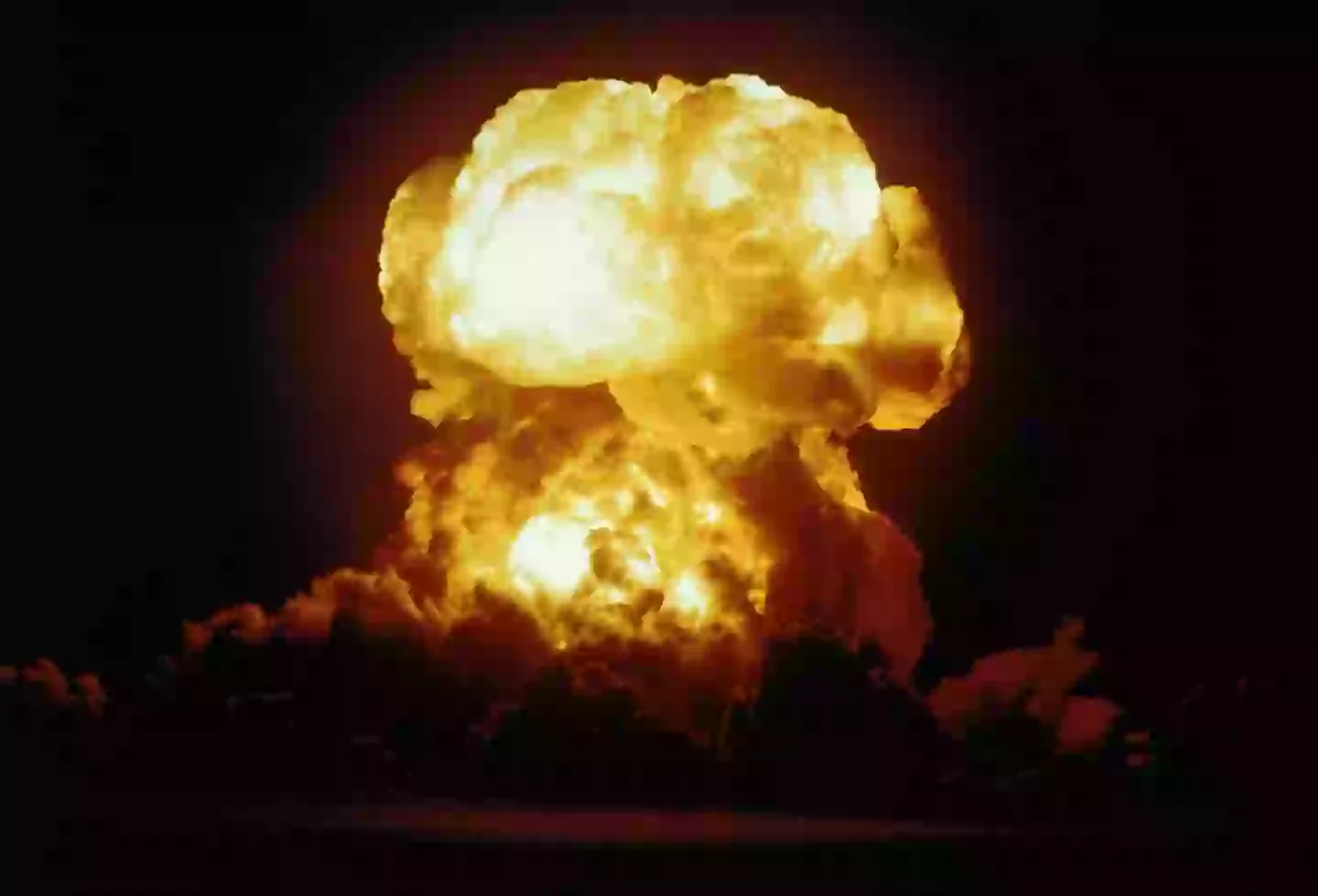

The US have held several nuclear bomb tests over the years (Getty Stock Photo)
All of this, in addition to the unresolved conflict between Russia and Ukraine, mean that whispers of another possible world war have not quietened down.
People are worried about the possibilities of nuclear warfare, which has the potential to wipe life off the face of the Earth.
We know that nuclear bombs were responsible for destroying both Hiroshima and Nagasaki, but many are unclear on how they really work.
You may have watched Oppenheimer, but the science involved was largely left out because who wants to hear about neutrons and isotopes for three hours?
A simulation posted on social media has revealed how the warheads work, and how they can cause severe damage.
How does a nuclear bomb work?
There are two types of nuclear bomb, an atomic bomb, which uses nuclear fission, and the hydrogen bomb, using nuclear fusion.
So far, only atomic bombs have been used in warfare. These weapons of mass destruction essentially encapsulate the forces that hold the nucleus of an atom together.
It does this by utilising the energy released when neutrons and protons, the particles that make up a nucleus, are split or merged together, according to Britannica.
The nucleus of an atom is split into two smaller fragments by a neutron, which can involve isotopes of uranium or plutonium, radioactive materials.
The process of nuclear fission is responsible for producing the atomic bomb, as when a single neutron strikes the nucleus of an atom of radioactive material, two or three neutrons are freed, releasing energy, with the cycle continuing.
You can see the process happen slowly in the simulation, as more energy is released with each strike of the nuclei, though this all happens instantaneously when detonated, as these fissions cause an explosion known as the atomic bomb.
How much damage can a nuclear bomb have?
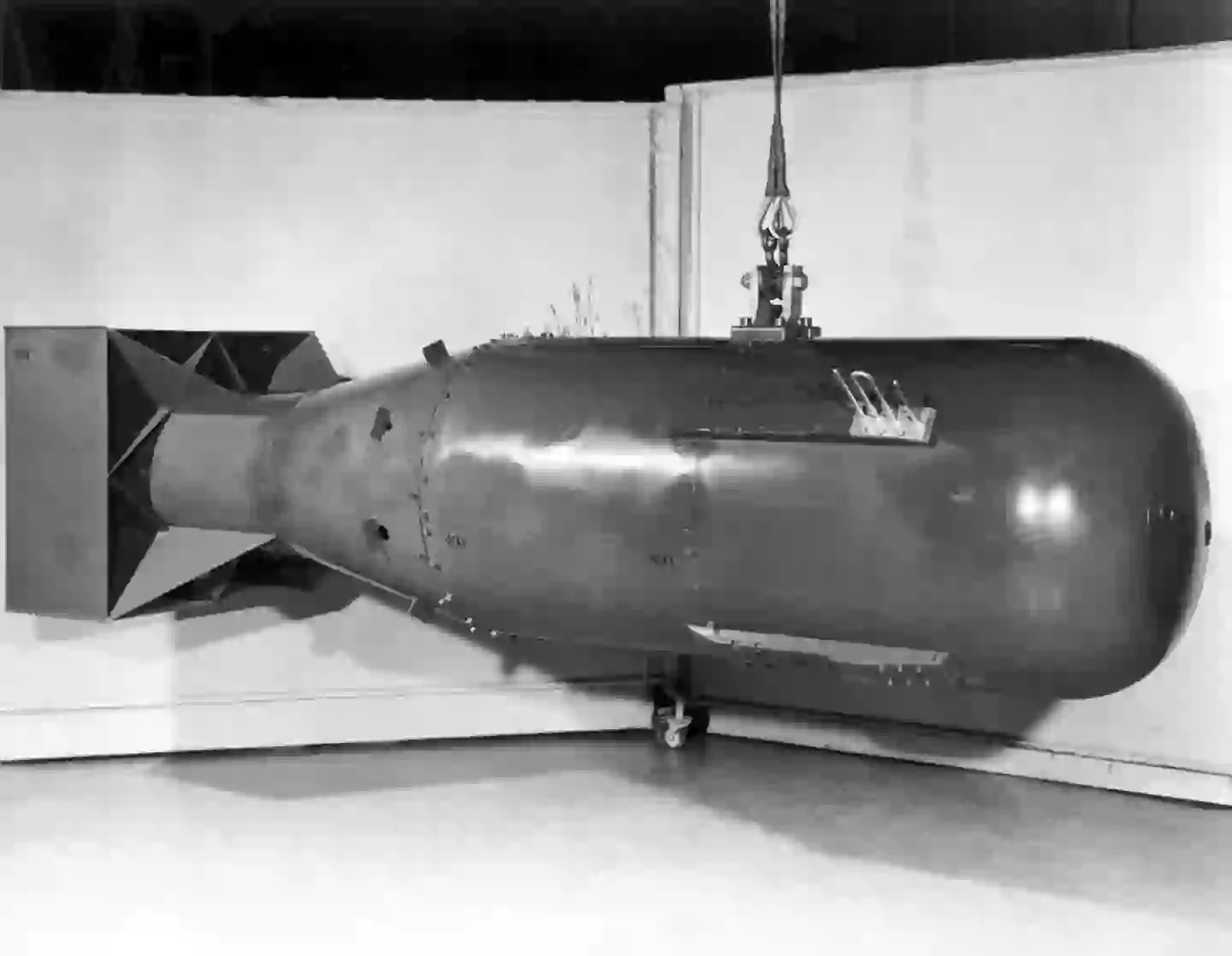

The ‘Little Boy’ nuclear bomb was dropped on Hiroshima in World War II (History/Universal Images Group via Getty Images)
According to Campain for Nuclear Disarmament (CNDUK), the heart of a nuclear explosion can reach numerous million degrees celsius, while creating a blast wave that causes a jump in air pressure, moving outward at thousands of miles an hour, gradually slowing down.
The heat flash over a certain area will vapourise all life, and those shielded will quickly be killed by the blast and heat, as the power can cause buildings to collapse.
Oxygen is sucked out of the atmosphere, suffocating those in underground shelters, while flammable materials catch fire.
While some further away from the point of impact will survive, many will suffer fatal burns, be blinded, or injured severely.
Others may succumb to radioactive fall-out, or even cancers caused by radiation, years later.
It is estimated that 90,000 to 166,000 people perished in the aftermath of the bombing of Hiroshima by the ‘Little Boy’ bomb, while 60,000 to 80,000 people died in Nagasaki.